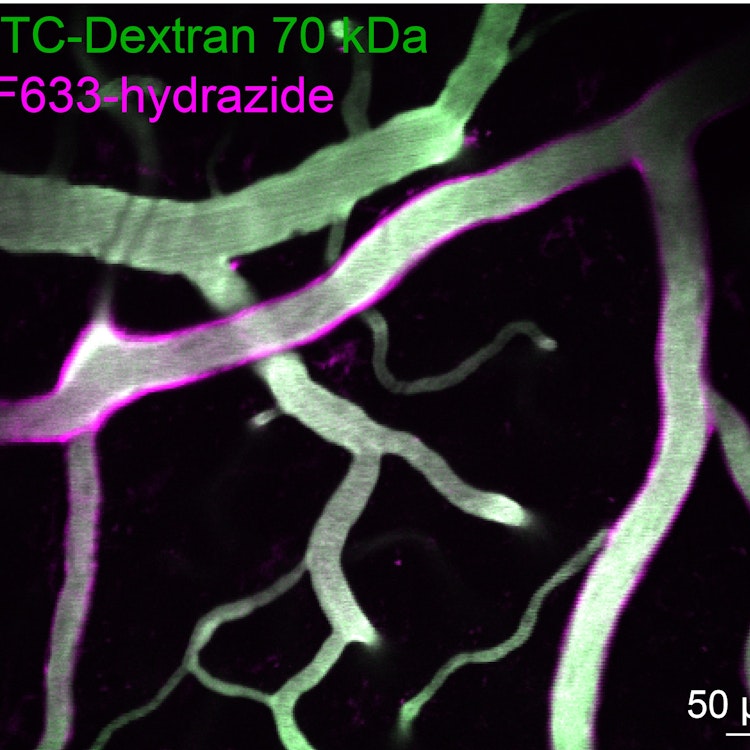
Interleukin-34-dependent perivascular macrophages promote vascular function in the brain
The development of most macrophages depends on the colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) receptor, which has two ligands: CSF-1 and interleukin-34 (IL-34). While IL-34 is required for the homeostasis of microglia, the parenchymal macrophages in the central nervous system (CNS), it is unclear whether brain border-associated macrophages (BAMs) also depend on this cytokine. Here, we demonstrated that the embryonic development of murine BAMs in the choroid plexus, leptomeninges, and perivascular spaces required CSF-1, while IL-34 was critical for their maintenance in adulthood. In the brain, Il34 was expressed by mural cells and perivascular fibroblasts, and its transgenic deletion in these cells interrupted BAM maintenance. Il34 deficiency coincided with transcriptional changes in vascular cells, leading to increased flow velocity and vasomotion in pial and penetrating arterioles. Similarly, Mrc1CreCsf1rfl/fl mice lacking CD206+ perivascular BAMs exhibited increased hemodynamics in arterial networks. These findings reveal a crosstalk between vascular cells and CNS macrophages regulating cerebrovascular function.
Download
vanhove_glueck_etal.pdfResearchers



